
How to manage eczema & support sensitive skin
Sabina JasinskiEczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition marked by a disrupted barrier, extreme dryness, itching, and flare-ups that can cause discomfort, discoloration, and even skin thickening over time. Though it can't be cured, it can absolutely be controlled—and your daily routine plays a central role in that.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through:
- What eczema is and how it affects your skin
- Common symptoms and flare-up triggers
- The essential steps of an eczema-friendly skincare routine
- When to seek medical help and how to treat flare-ups
- Lifestyle habits that support long-term skin health
- And common myths to stop believing right now
Let’s start by understanding what eczema really is—beneath the surface.
WHAT is eczema?
Eczema is not just dry skin—it’s a complex barrier and immune dysfunction. At its core, eczema is a genetic + environmental condition where:
- The skin produces fewer lipids and ceramides
- The barrier is “leaky”, allowing allergens, bacteria, and irritants to enter
- The immune system overreacts, leading to inflammation, itch, and visible flare-ups
This cycle of dryness → irritation → scratching → more barrier damage is what creates the classic eczema flare.
WHAT CAUSES FLARE-UPS?
Atopic dermatitis is highly individual, but most flare-ups are triggered by a combination of:
- Irritants: Fragrance, essentiall oils, sulfates, preservatives (e.g. parabens, MCI/MI)
- Environment: Dry or cold weather, heat, sudden humidity shifts
- Allergens: Dust mites, pet dander, pollen, mold
- Stress: Emotional triggers increase cortisol, which weakens the barrier
- Overwashing: Hot water, harsh cleansers, or excessive exfoliation
- Diet sensitives: For some: dairy, gluten, soy, nuts (varies individually)
🔍 Eczema symptoms can include:
-
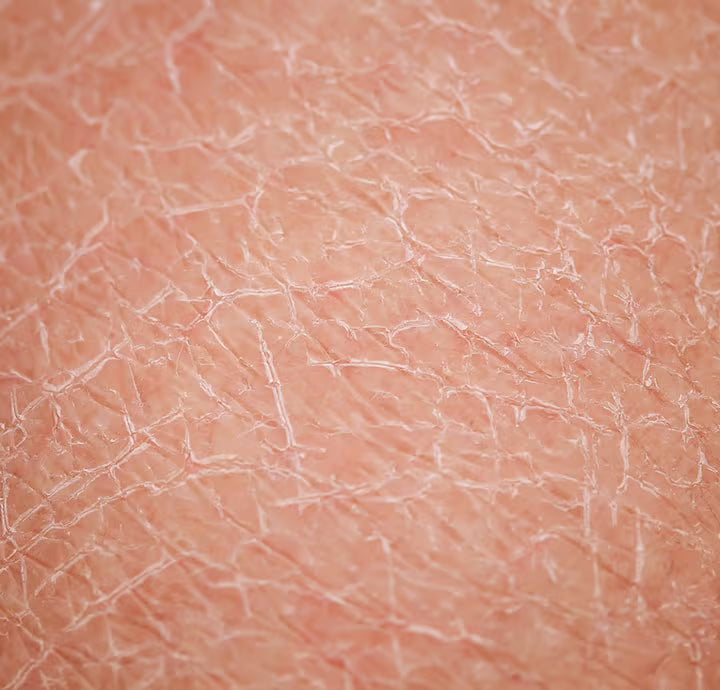
1. Dry, tight, or “cracked” skin
This can also be referred to as xerosis or dry skin, often leading to rough, flaky patches that may feel tight, especially after bathing.
-
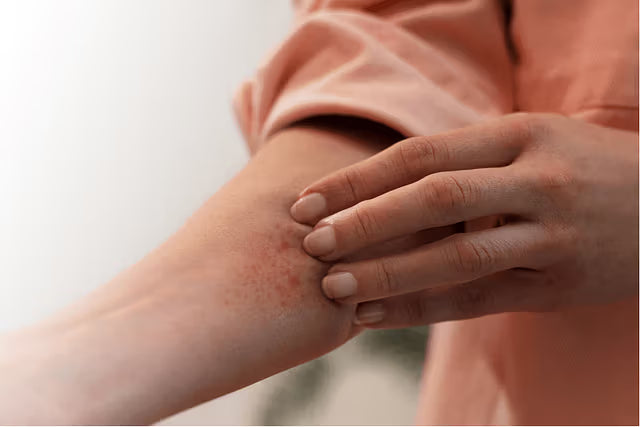

2. Intense, persistent itching
Known medically as pruritus, this intense itching is one of the hallmark symptoms of eczema, often exacerbated at night or during flare-ups.
-
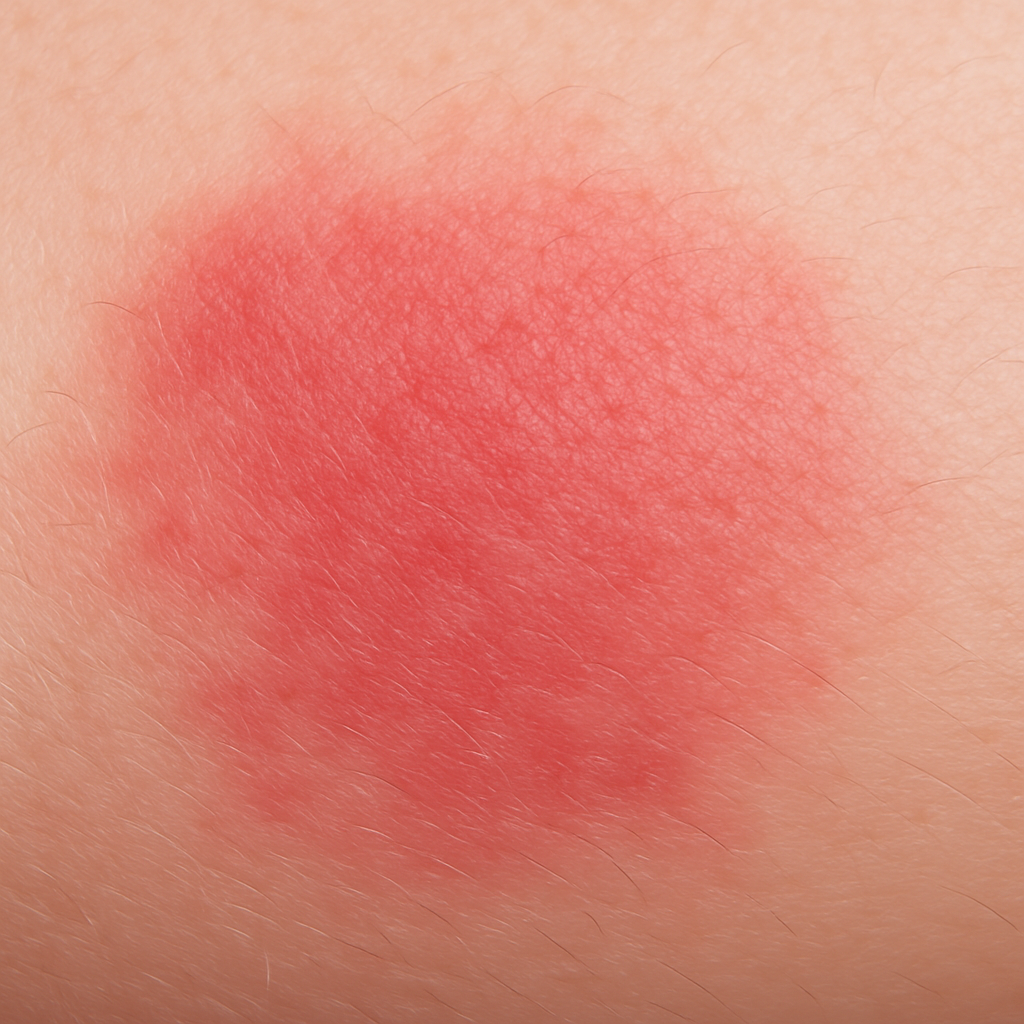
3. Red, inflamed patches
These patches are referred to as erythema, where the skin appears red or inflamed. This is especially common in the acute stages of eczema, as the skin reacts to irritation or allergens.
-
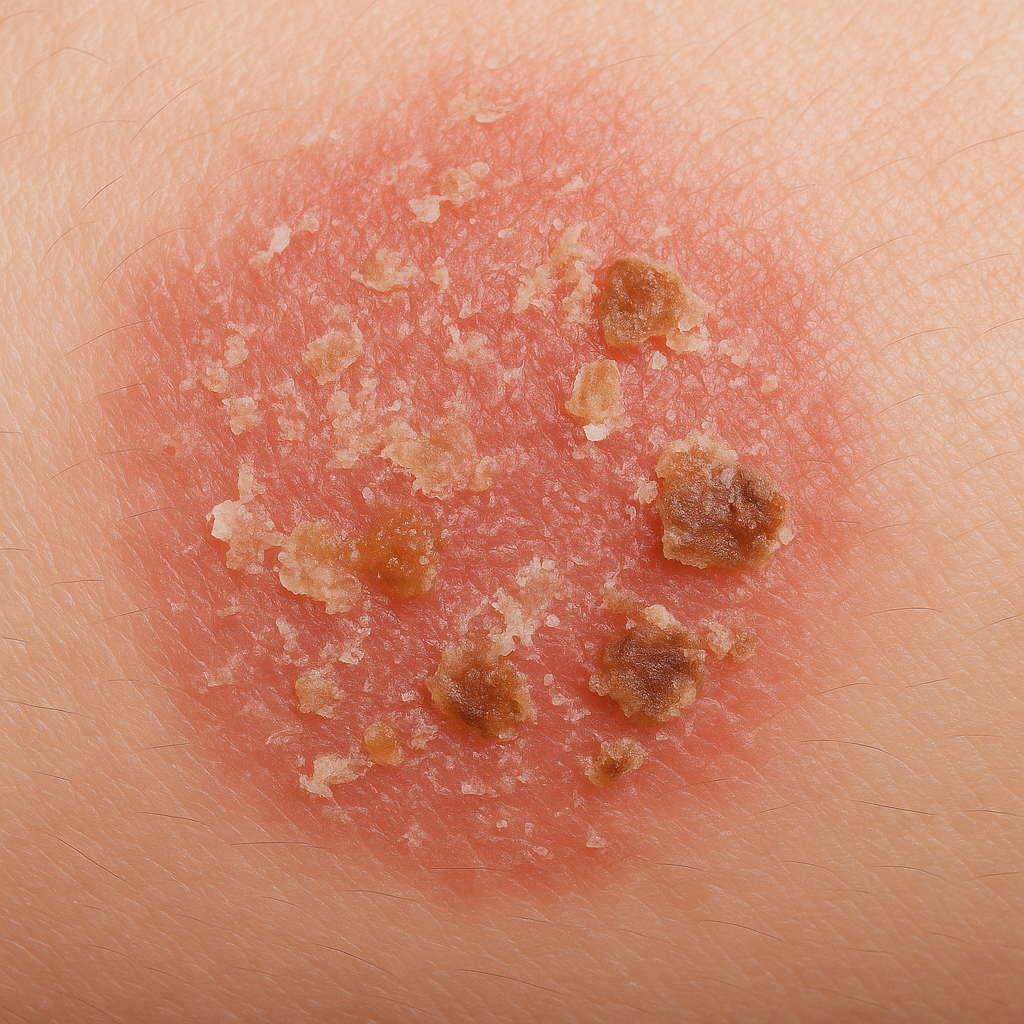
4.. Scaling, flaking, or oozing
In more severe or acute stages, eczema may cause desquamation (scaling or flaking), and in cases of eczema herpeticum, the skin can ooze fluid due to secondary infection. This can lead to crusting and scabbing.
-
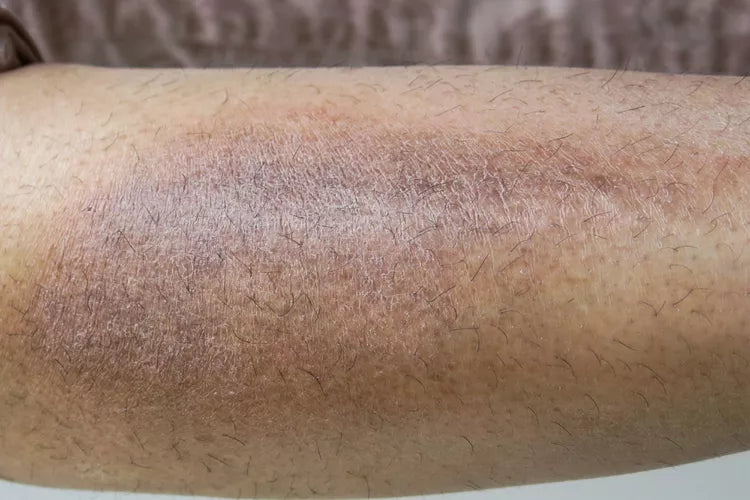
5. Skin thickening or discoloration
Chronic eczema can lead to lichenification, a process where the skin becomes thickened due to repeated scratching or rubbing. Additionally, discoloration may occur in the form of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (darker patches) or hypopigmentation (lighter patches) after healing.
Skincare Solutions for specific symtoms:
1. Dry, Tight, or “Cracked” Skin (Xerosis)
Skincare Solutions:
- Moisturizing is essential: Use thick, emollient creams or ointments (like petroleum jelly or Aquaphor) to lock in moisture. These should be applied immediately after bathing when the skin is still damp to trap hydration.
- Hyaluronic acid helps attract moisture to the skin, while glycerin aids in hydration.
- Ceramide-based creams are ideal as they repair the skin barrier and help prevent further moisture loss.
- Humidifiers in the home can add moisture to the air, preventing the skin from becoming too dry in low-humidity environments.
2. Intense, Persistent Itching (Pruritus)
- Anti-itch creams: Use products containing hydrocortisone (mild topical steroids) or pramoxine (a topical anesthetic) to reduce itching and inflammation.
- Cooling gels or creams with menthol or calamine can offer immediate relief.
- Colloidal oatmeal baths can soothe the skin and reduce irritation. Look for products like Aveeno or Eucerin that contain this ingredient.
- Moisturizing regularly will prevent dryness and minimize itching caused by dryness.
- Avoid scratching: Cutting nails short and using cotton gloves at night can help prevent further damage from scratching.
3. Red, Inflamed Patches (Erythema)
- Topical corticosteroids: Use these as prescribed by a doctor to reduce inflammation. For more sensitive areas, non-steroidal treatments like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can be used as alternatives.
- Soothing moisturizers with aloe vera or calendula extract can help calm inflammation.
- Cool compresses can provide temporary relief from redness and inflammation, reducing the appearance of erythema.
- Fragrance-free, gentle cleansers that do not strip the skin of its natural oils are important to avoid further irritation.
4. Scaling, Flaking, or Oozing (Desquamation/Eczema Herpeticum)
- Moisturizing: As eczema flares up, the skin loses its ability to retain moisture. Use thick creams or oils (like jojoba oil, coconut oil, or shea butter) to prevent further scaling.
- Antiseptic creams or ointments: To prevent infection from oozing or open sores, use creams with mupirocin or hydrocortisone.
- Gentle exfoliation: Once the skin has healed a bit, you can gently exfoliate with a soft washcloth or gentle exfoliant to remove flaky skin. However, avoid doing this during flare-ups to prevent further irritation.
- Antiviral treatments: If eczema herpeticum is suspected (when eczema is complicated by a viral infection), antiviral creams or oral antiviral medications prescribed by a doctor are necessary.
5. Skin Thickening or Discoloration (Lichenification/Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation)
- Topical steroids: Use low-potency corticosteroids as prescribed to help reduce skin thickening or lichenification. For sensitive areas, calcineurin inhibitors may be more appropriate.
- Moisturizing: Keep the skin hydrated to prevent further thickening of the skin.
- Vitamin C serums: For post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (darker spots), products with vitamin C can help brighten the skin and fade discoloration.
- Retinoids: If approved by a dermatologist, retinoid-based creams can help with cell turnover and lighten darker patches (though they should be used cautiously in sensitive skin).
- Exfoliating acids: AHAs (like lactic acid) or BHAs (like salicylic acid) can help in the long-term treatment of skin thickening, but use sparingly to avoid irritation.
Evidence-Backed treatments
1. FOCUS ON BARRIER-FIRST CLEANSING
Cleansing is necessary—but in eczema, it must be done without stripping. This means:
- No foaming agents (SLS/SLES)
- No fragrance or essential oils
- No high-pH cleansers (they worsen barrier disruption)
✅ Instead, look for:
- Creamy, soap-free cleansers
- Colloidal oatmeal, glycerin, panthenol, or shea butter
- Micellar waters for ultra-sensitive skin (no rinse required)
🧼 Limit cleansing to once daily in the evening unless skin is visibly dirty.
2. REBUILD THE BARRIER WITH STRATEGIC MOISTURISING
Moisturising isn’t just about hydration—it’s one of the most important steps in managing eczema. Eczema-prone skin lacks essential lipids like ceramides, fatty acids, and natural moisturising factors (NMFs) that help it stay strong and resilient.
To properly support the skin barrier, your moisturiser should include a mix of:
- Humectants – These ingredients pull moisture into the skin, helping to rehydrate dry, tight areas. → Look for glycerin, hyaluronic acid, or urea.
- Emollients – These soften and smooth the skin by filling in tiny gaps between skin cells, making skin feel more flexible and less rough. → Great options include squalane, sunflower oil, or colloidal oatmeal.
- Occlusives – These form a protective layer on the surface of the skin to seal in moisture and prevent water loss. → Common occlusives are petrolatum (Vaseline), lanolin, or dimethicone.
You don’t always need to find all three (humectant, emollient, occlusive) in one product, but it’s ideal if your routine includes all three — whether:
- They’re all in one well-formulated moisturiser
- Or you layer multiple products that provide each function
✅ Option 1: All-in-One Moisturiser
Some moisturisers are formulated with humectants + emollients + occlusives already built in — which is great for simplicity.
Look for products that include:
- Glycerin or hyaluronic acid (humectants)
- Squalane, sunflower oil, or colloidal oatmeal (emollients)
- Petrolatum, lanolin, or dimethicone (occlusives)
💡 Many eczema creams (like CeraVe, Eucerin, or La Roche-Posay Lipikar) are designed this way.
✅ Option 2: Layering Products
If your moisturiser only contains some of these, you can layer to get full barrier support:
- Start with a hydrating serum (like hyaluronic acid or panthenol)
- Follow with your moisturiser (rich in emollients like squalane or oat oil)
- Finish with a thin layer of an occlusive balm (like Vaseline or lanolin) on top — especially on dry patches
This is especially useful during flare-ups or very dry weather.
💡 Pro tip: Always apply your moisturiser within 3 minutes after bathing, while your skin is still slightly damp. This method—called “soak and seal”—helps lock in the water your skin just absorbed and gives better long-term hydration.
3. CALM INFLAMMATION—GENTLY AND CONSISTENTLY
During flare-ups, it's critical to soothe without triggering. Anti-inflammatory actives must be gentle and barrier-safe.
Best options include:
- Colloidal oatmeal – anti-inflammatory, anti-itch
- Panthenol (Vitamin B5) – promotes healing and hydration
- Allantoin – reduces stinging and burning
- Centella asiatica – calms redness and supports tissue regeneration
- Niacinamide (low concentration, 2–5%) – helps reduce itching and improve barrier resilience
✅ Avoid all acids, retinoids, essential oils, and harsh preservatives.
4. When to See a Doctor 🩺
While daily skincare plays a key role in managing eczema, there are times when professional medical guidance is essential. Contact a dermatologist or healthcare provider if you experience:
- Frequent or severe flare-ups that don’t improve with OTC products
- Cracked, bleeding, or oozing skin, which may indicate infection
- Spreading rashes or intense itching that disrupts sleep or daily life
- No improvement after 2–3 weeks of consistent care
- The need for prescription therapies or diagnosis of potential allergies
💡 Your doctor can also help identify hidden triggers, offer stronger anti-inflammatories, or refer you to allergy testing if needed.
5. TREAT FLARE-UPS WITH TARGETED THERAPY
While daily care focuses on prevention, eczema flare-ups often require short-term anti-inflammatory treatments to calm redness, swelling, and discomfort.
🩺 Topical Treatments:
- Hydrocortisone (OTC): Mild inflammation relief
- Prescription topical steroids: E.g., betamethasone or triamcinolone—effective but must be tapered carefully
- Calcineurin inhibitors: E.g., tacrolimus or pimecrolimus—steroid alternatives, safe for long-term use on delicate areas
- Topical antibiotics: If there’s broken skin or signs of infection
💡 Additional Support:
- Wet wrap therapy: Apply moisturiser or medication, then wrap skin in damp gauze to enhance penetration and soothe inflammation
- Antihistamines: May reduce nighttime itching and support sleep
- Phototherapy (narrowband UVB): For severe or widespread eczema under specialist care
🌞 MORNING: Soothe, Protect, and Strengthen the Barrier
1. Ultra-Gentle Cleanser
Cleans without stripping or aggravating the skin’s compromised barrier.
- Choose cream or balm cleansers
- Look for glycerin, colloidal oatmeal, panthenol, or shea butter
- Avoid sulfates, fragrance, essential oils, and anything that foams excessively
💡 In the morning, you can even rinse with just lukewarm water if your skin isn't oily—especially during flare-ups.
-
2. Soothing Serum or Hydrating Mist (optional)
If your skin tolerates it, this is where you can add a lightweight layer of hydration.
- Panthenol, beta-glucan, oat extract, or thermal water mists
- No actives, no fragrance—just calming, anti-inflammatory hydration
💡 Skip this step during active flare-ups unless your skin feels dry and tight.
-
3. Barrier-Repair Moisturiser
The heart of your routine. A thick, rich moisturiser supports healing and keeps inflammation at bay.
Choose fragrance-free creams with:
- Ceramides
- Squalane, colloidal oatmeal, shea butter
- Urea or glycerin for extra hydration
💡 Apply generously and reapply throughout the day on dry patches or after washing.
-
4. Mineral Sunscreen SPF 30–50
Eczema skin still needs sun protection, but it must be gentle.
- Choose zinc oxide or titanium dioxide-based sunscreens
- Look for formulas labeled fragrance-free, alcohol-free, and non-nano
- Tinted mineral formulas can also help calm visible redness
💡 If sunscreen stings, apply a light layer of moisturiser first to buffer.
🌙 EVENING: Replenish, Calm, and Restore the Skin
1. Cleanser
Stick to your morning cleanser—keep it fragrance-free and creamy.
💡 If you wore makeup or sunscreen, consider gentle double cleansing: use a mild cleansing balm first, followed by your regular cleanser. Skip this if skin is flaring.
-
2. Calming Treatment Layer (if needed)
This step can include:
- Colloidal oatmeal lotion
- Centella asiatica or panthenol-based serums
- Prescription creams (e.g. hydrocortisone, tacrolimus)—as directed by your doctor
💡 Only use active treatment here if you’re addressing a flare-up. Otherwise, keep this step minimal.
-
3. Barrier-Rich Moisturiser
Apply a thick, nourishing moisturiser all over—especially on dry zones, hands, and flex areas (elbows, knees).
Look for:
- Ceramides
- Cholesterol + fatty acids
- Lanolin, squalane, urea, or shea butter
-
4. Occlusive Balm (optional)
Seal in moisture with an occlusive layer on dry or cracked areas.
- Use Vaseline (petrolatum), lanolin, or thick barrier balms
- Especially helpful for hands, eyelids, lips, and flare-prone areas
💡 Great for overnight repair and preventing trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL).
💡 BONUS CARE TIPS:
- Double cleanse? Only when needed. If wearing SPF or makeup, use a fragrance-free cleansing oil followed by your regular cleanser.
- Short, lukewarm showers only—hot water strips the skin barrier.
- Avoid wool, polyester, and scratchy fabrics. Stick to soft, breathable cotton.
- Use a humidifier during dry seasons to reduce environmental triggers.
- Patch test everything. Even "eczema-safe" products can cause reactions in certain individuals.
- Trim nails or wear cotton gloves at night to avoid skin damage from scratching.
⏱️ WHEN TO EXPECT RESULTS
- Retinoids & peptides – noticeable results in 8–12 weeks
- Hydrating serums – plumping effect in days
- Professional treatments (microneedling, laser, radiofrequency) – multiple sessions often needed
- SPF – protects instantly and prevents further degradation
- Moisturisers & barrier creams - Relief within days; skin strengthening in 2–4 weeks
- Topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors - Redness & itching often reduced within 1–3 days
- Lifestyle adjustments (humidifier, laundry, fabrics) - Reduced flares in 1–2 weeks
- Long-term maintenance - Fewer relapses and improved resilience in 4–8 weeks
🧘🏾♀️ Lifestyle Habits to Support Eczema-Prone Skin
Managing eczema isn’t just about skincare—it’s also about supporting your skin from the inside out and avoiding triggers in your environment. Here’s how you can reduce flare-ups and help your skin stay calm, hydrated, and resilient.
1. Keep Stress in Check
Emotional stress is a well-documented eczema trigger. High cortisol levels can weaken the skin barrier and increase inflammation.
Try calming practices like:
- Breathwork or meditation
- Gentle movement (yoga, walking)
- Journaling or quiet screen-free time before bed
2. Avoid Harsh Fabrics & Friction
Eczema-prone skin is especially reactive to physical irritation.
🟢 Choose:
- Soft, breathable fabrics like cotton or bamboo
- Tagless clothing and seamless underwear
- Loose-fitting layers, especially during flares
🟡 Avoid: Wool, synthetic fibers, tight waistbands, and scratchy seams.
3. Prioritise Gentle Laundry Habits
Laundry detergents can leave residue that irritates sensitive skin.
Best practices:
- Use fragrance-free, dye-free detergents
- Avoid fabric softeners (which often contain hidden irritants)
- Double-rinse laundry if you’re extra sensitive
4. Support Skin Through Diet (if relevant to your body)
Not everyone with eczema has food sensitivities—but in some, diet plays a role.
🟢 Focus on:
- Anti-inflammatory foods (omega-3s from salmon, flaxseed, walnuts)
- Hydrating foods (cucumbers, berries, leafy greens)
- Probiotics (yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut) for gut support
🛑 If you suspect food triggers (e.g. dairy, eggs, gluten), consult a doctor or nutritionist before eliminating.
5. Use a Humidifier
Dry indoor air (especially in winter or with air conditioning) can worsen eczema.
- Keep humidity around 40–50%
- Use a humidifier in your bedroom while you sleep for overnight barrier support
6. Sleep Hygiene Matters
Eczema can worsen at night due to body temperature changes and itching.
Tips for better rest:
- Keep your bedroom cool and breathable
- Use soft bedding, washed with fragrance-free detergent
- Apply a soothing moisturiser or balm before bed
- Wear cotton gloves or long sleeves if scratching is a problem
7. Stay Consistent—Even When Your Skin Looks “Good”
Eczema is chronic and cyclical. Even during clear-skin periods, daily barrier support is essential.
- Stick to fragrance-free moisturising
- Avoid reintroducing known triggers
- Keep your skin protected against weather, friction, and dehydration
❌ Common Myths About eczema
“You need to scrub the flakes off.”
❌ Absolutely not. Scrubbing damages already compromised skin and increases inflammation.
-
“Steroids thin your skin no matter what.”
❌ Nope. Only long-term misuse of strong steroids causes this. Proper, supervised use is effective and safe.
-
“Natural products are safer.”
🟡 Not always. Many contain essential oils or allergens that trigger flare-ups. “Natural” isn’t always “gentle.”
💚 Final Thoughts
Eczema is a lifelong skin condition—but with the right care, your skin can absolutely become stronger, calmer, and more comfortable. Focus on barrier restoration, avoiding triggers, and responding early to flares for the best long-term results.
Because your skin deserves more than just temporary relief—it deserves consistent care, patience, and protection.
Guides to healthier skin:
Skin Concerns Series
From hyperpigmentation to hydration, the Skin Concerns Series by Know to Glow breaks down common skincare issues with clarity, science, and strategy.
Each guide is designed to help you understand the root causes, avoid common mistakes, and build a routine that actually works.
Skin Concerns Series
KNOW TO GLOW = SCIENCE+EDUCATION
Know to Glow is both a shop and a hub for essential skincare knowledge. Our goal is to help you achieve healthy skin by understanding the biology behind skincare—what nourishes it and what can compromise it.









